

电子说
本篇是对UVM设计模式 ( 二 ) 参数化类、静态变量/方法/类、单例模式、UVM_ROOT、工厂模式、UVM_FACTORY[1]中单例模式的补充,分析静态类的使用,UVM中资源池的实现,uvm_config_db的使用。
Static class
Systemverilog中可以使用static修饰变量,方法,得到静态变量和静态函数。static也可以直接修饰class,获得静态类。但是static class class_name .... endclass这种直接定义一个静态类的方式是不允许的,只可以在一个class的内部,通过static class_name的方式声明一个静态类。这一点SV与Java相同。(Java中的 static class[2])
静态类的特征:
1.相比automatic class, 静态类被new创建后,其对应的内存空间一直存在,伴随仿真结束。配合单例模式使用,则是全局唯一类的实例,可以被当作全局变量使用。2.相比静态变量,静态类可以封装更多内容,充当资源容器的角色。
所以UVM中对全局的资源管理,都是通过静态类实现的。
uvm_pool
uvm_pool#(type KEY=int, T=uvm_void)是一个参数化的类,相当于SV中的联合数组。参数KEY是联合数组的索引,参数T是联合数组存储的变量类型。uvm_pool封装了原有联合数组的操作方法,供访问内部的联合数组pool。 m_global_pool是uvm_pool #(KEY, T)类型的静态类,通过静态方法get_global_pool可以获得唯一的实例。 uvm_queue #(T)和uvm_pool#(type KEY=int, T=uvm_void)类似,实现一个class-based dynamic queue.
# uvm_pool.svh
class uvm_pool #(type KEY=int, T=uvm_void) extends uvm_object;
const static string type_name = "uvm_pool";
typedef uvm_pool #(KEY,T) this_type;
static protected this_type m_global_pool;
protected T pool[KEY];
// Function: new
// Creates a new pool with the given ~name~.
function new (string name="");
super.new(name);
endfunction
// Function: get_global_pool
// Returns the singleton global pool for the item type, T.
// This allows items to be shared amongst components throughout the
// verification environment.
static function this_type get_global_pool ();
if (m_global_pool==null)
m_global_pool = new("pool");
return m_global_pool;
endfunction
// Function: get_global
// Returns the specified item instance from the global item pool.
static function T get_global (KEY key);
this_type gpool;
gpool = get_global_pool();
return gpool.get(key);
endfunction
// Function: get
// Returns the item with the given ~key~.
// If no item exists by that key, a new item is created with that key
// and returned.
virtual function T get (KEY key);
if (!pool.exists(key)) begin
T default_value;
pool[key] = default_value;
end
return pool[key];
endfunction
virtual function void add (KEY key, T item);
pool[key] = item;
endfunction
virtual function int num ();
return pool.num();
endfunction
......
......
......
endclass
uvm_event_pool
uvm_object_string_pool的KEY是string类型。 uvm_event_pool由uvm_object_string_pool #(uvm_event)声明,KEY是string类型,T是uvm_event类型。 uvm_event是sv中event的class warpper,内建了很多方法。
# uvm_pool.svh class uvm_object_string_pool #(type T=uvm_object) extends uvm_pool #(string,T); ...... typedef class uvm_barrier; typedef class uvm_event; typedef uvm_object_string_pool #(uvm_barrier) uvm_barrier_pool; typedef uvm_object_string_pool #(uvm_event) uvm_event_pool;
# uvm_event.svh
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CLASS: uvm_event
// The uvm_event class is a wrapper class around the SystemVerilog event
// construct. It provides some additional services such as setting callbacks
// and maintaining the number of waiters.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class uvm_event extends uvm_object;
const static string type_name = "uvm_event";
local event m_event;
local int num_waiters;
local bit on;
local time trigger_time=0;
local uvm_object trigger_data;
local uvm_event_callback callbacks[$];
function new (string name="");
super.new(name);
endfunction
......
......
......
virtual task wait_on (bit delta=0);
virtual task wait_off (bit delta=0);
virtual task wait_trigger ();
virtual task wait_ptrigger ();
virtual task wait_trigger_data (output uvm_object data);
virtual task wait_ptrigger_data (output uvm_object data);
virtual function void trigger (uvm_object data=null);
virtual function uvm_object get_trigger_data ();
virtual function time get_trigger_time ();
virtual function void add_callback (uvm_event_callback cb, bit append=1);
virtual function int get_num_waiters ();
......
endclass : uvm_event
使用
uvm_event_pool作为全局唯一的uvm_evnet的资源池,可以在不同component中调用,实现事件的同步功能。比如sequence和scoreboard需要通过event来握手:
# event_sequence.sv
class event_sequence extends uvm_sequence;
......
uvm_event_pool events_pool;
uvm_event sync_e;
......
function new (string name = "event_sequence");
events_pool = uvm_event_pool::get_global_pool();
sync_e = events_pool.get("sync_e");
// 也可以直接调用 sync_e = uvm_event_pool::get_global("sync_e");
endfunction
......
virtual task body();
......
sync_e.trigger();
......
endtask
endclass
# event_scb.sv
class event_scb extends uvm_scoreboard;
......
uvm_event_pool events_pool;
uvm_event sync_e;
......
function new (string name = "event_sequence");
events_pool = uvm_event_pool::get_global_pool();
sync_e = events_pool.get("sync_e");
endfunction
......
virtual task wait_sync_e();
......
sync_e.wait_trigger();
......
endtask
endclass
无论是uvm_component还是uvm_object,是否在同一个package中,都可以通过uvm_evnet_pool::get_global_pool()获得全局唯一的uvm_event资源池。上述的uvm_event并不需要new(),因为调用get()函数时会自动创建:
# uvm_object_string_pool #(uvm_event)
// Function: get
// Returns the object item at the given string ~key~.
// If no item exists by the given ~key~, a new item is created for that key
// and returned.
virtual function T get (string key);
if (!pool.exists(key))
pool[key] = new (key);
return pool[key];
endfunction
uvm_event不仅可以用于event同步,也可以传递一些简单的数据。提供了两个方法:wait_trigger_data (output uvm_object data) trigger (uvm_object data),可以传递uvm_object类型的数据。也可以add_callback加入回调函数。 uvm_event[3] uvm中还提供了uvm_barrier用于多个组件之间的同步,uvm_barrier_pool存放所有的uvm_barrier。
uvm_config_db
结构
uvm_resource#(type T): 各类资源(*scalar objects class handles queues lists virtual interfaces 等*)的一个wrapper,内部成员变量val是一个type T类型的句柄,通过调用write函数,将val指向资源的实例( *!!! 对于class handles virtual interfaces,val看作句柄指向实例;对于 queues lists等,val是被直接赋值 !!!*)。set函数将uvm_resource加入全局资源池uvm_resources。
class uvm_resource #(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_base;
typedef uvm_resource#(T) this_type;
// singleton handle that represents the type of this resource
static this_type my_type = get_type();
// Can't be rand since things like rand strings are not legal.
protected T val;
......
// Function: get_type
// Static function that returns the static type handle. The return
// type is this_type, which is the type of the parameterized class.
static function this_type get_type();
if(my_type == null)
my_type = new();
return my_type;
endfunction
......
// Function: set
// Simply put this resource into the global resource pool
function void set();
uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get();
rp.set(this);
endfunction
......
// Function: write
// Modify the object stored in this resource container. If the
// resource is read-only then issue an error message and return
// without modifying the object in the container. If the resource is
// not read-only and an ~accessor~ object has been supplied then also
// update the accessor record. Lastly, replace the object value in
// the container with the value supplied as the argument, ~t~, and
// release any processes blocked on
// . If the value to be written is
// the same as the value already present in the resource then the
// write is not done. That also means that the accessor record is not
// updated and the modified bit is not set.
function void write(T t, uvm_object accessor = null);
if(is_read_only()) begin
uvm_report_error("resource", $sformatf("resource %s is read only -- cannot modify", get_name()));
return;
end
// Set the modified bit and record the transaction only if the value
// has actually changed.
if(val == t)
return;
record_write_access(accessor);
// set the value and set the dirty bit
val = t;
modified = 1;
endfunction
......
uvm_resource_pool: 存放所有的uvm_resource, 全局唯一的实例uvm_resources。 uvm_resource_pool::get()得到uvm_resources。(注意: 这里的 new函数使用了local修饰,而uvm_event_pool中的 new没有被 local修饰。所以 uvm_resource_pool和 uvm_root拥有真正的全局唯一实例,而uvm_event_pool可以在外部手动 new创建多个实例。)
rtab[string] ttab[uvm_resource_base]分别以name type为索引存放uvm_resource。
//---------------------------------------------------------------------- // Class: uvm_resource_pool // // The global (singleton) resource database. // // Each resource is stored both by primary name and by type handle. The // resource pool contains two associative arrays, one with name as the // key and one with the type handle as the key. Each associative array // contains a queue of resources. Each resource has a regular // expression that represents the set of scopes over with it is visible. // //| +------+------------+ +------------+------+ //| | name | rsrc queue | | rsrc queue | type | //| +------+------------+ +------------+------+ //| | | | | | | //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ +------------+------+ //| | | | | | |<--+---* | T | //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ +-+-+ +------------+------+ //| | A | *---+-->| | | | | | | //| +------+------------+ +-+-+ | +------------+------+ //| | | | | | | | | //| +------+------------+ +-------+ +-+ +------------+------+ //| | | | | | | | | //| +------+------------+ | | +------------+------+ //| | | | V V | | | //| +------+------------+ +------+ +------------+------+ //| | | | | rsrc | | | | //| +------+------------+ +------+ +------------+------+ // // The above diagrams illustrates how a resource whose name is A and // type is T is stored in the pool. The pool contains an entry in the // type map for type T and an entry in the name map for name A. The // queues in each of the arrays each contain an entry for the resource A // whose type is T. The name map can contain in its queue other // resources whose name is A which may or may not have the same type as // our resource A. Similarly, the type map can contain in its queue // other resources whose type is T and whose name may or may not be A. // // Resources are added to the pool by calling; they are retrieved // from the pool by calling or . When an object // creates a new resource and calls the resource is made available to be // retrieved by other objects outside of itsef; an object gets a // resource when it wants to access a resource not currently available // in its scope.
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
// static global resource pool handle
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
const uvm_resource_pool uvm_resources = uvm_resource_pool::get();
class uvm_resource_pool;
static bit m_has_wildcard_names;
static local uvm_resource_pool rp = get();
uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rtab [string];
uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t ttab [uvm_resource_base];
......
local function new();
endfunction
// Function: get
//
// Returns the singleton handle to the resource pool
static function uvm_resource_pool get();
if(rp == null)
rp = new();
return rp;
endfunction
......
// Function: get_by_name
//
// Lookup a resource by ~name~, ~scope~, and ~type_handle~. Whether
// the get succeeds or fails, save a record of the get attempt. The
// ~rpterr~ flag indicates whether to report errors or not.
// Essentially, it serves as a verbose flag. If set then the spell
// checker will be invoked and warnings about multiple resources will
// be produced.
function uvm_resource_base get_by_name(string scope = "",
string name,
uvm_resource_base type_handle,
bit rpterr = 1);
// Function: get_by_type
//
// Lookup a resource by ~type_handle~ and ~scope~. Insert a record into
// the get history list whether or not the get succeeded.
function uvm_resource_base get_by_type(string scope = "",
uvm_resource_base type_handle);
......
......
endclass
uvm_resource_db#(type T):访问资源池的接口,内部都是static function。
uvm_config_db#(type T):继承于uvm_resource_db#(type T),进行了一些功能扩展。内部都是static function。
接下来重点看一下uvm_config_db传入的4个参数:
cntxt: uvm_component类型,context上下文的含义,由cntxt可以确定资源的优先级,对同一个资源set,从UVM树顶层往下,优先级依次降低。cntxt = null时,为uvm_root::get(),优先级最高。
inst_name: string类型,通过{cntxt.get_full_name(), ".", inst_name}组成的字符串设置资源的scope。内部调用DPI,支持通配符。只有get中的scope可以和set中的scope匹配上,才可以正常访问资源。
field_name: 资源名,scope内的资源。也支持通配符,一般set get设置相同即可。
value: type T类型,资源的类型。get中的是inout,调用get函数先给value赋值,结束后再将val传出,但是get中并没有处理传入value的代码,不知道为什么这样用。
class uvm_config_db#(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_db#(T);
......
static uvm_pool#(string,uvm_resource#(T)) m_rsc[uvm_component];
......
static function bit get(uvm_component cntxt,
string inst_name,
string field_name,
inout T value);
//TBD: add file/line
int unsigned p;
uvm_resource#(T) r, rt;
uvm_resource_pool rp = uvm_resource_pool::get();
uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rq;
if(cntxt == null)
cntxt = uvm_root::get();
if(inst_name == "")
inst_name = cntxt.get_full_name();
else if(cntxt.get_full_name() != "")
inst_name = {cntxt.get_full_name(), ".", inst_name};
......
value = r.read(cntxt);
return 1;
endfunction
static function void set(uvm_component cntxt,
string inst_name,
string field_name,
T value);
uvm_root top;
uvm_phase curr_phase;
uvm_resource#(T) r;
bit exists;
string lookup;
uvm_pool#(string,uvm_resource#(T)) pool;
//take care of random stability during allocation
process p = process::self();
string rstate = p.get_randstate();
top = uvm_root::get();
curr_phase = top.m_current_phase;
if(cntxt == null)
cntxt = top;
if(inst_name == "")
inst_name = cntxt.get_full_name();
else if(cntxt.get_full_name() != "")
inst_name = {cntxt.get_full_name(), ".", inst_name};
......
r.write(value, cntxt);
......
endfunction
有一种特殊的情况,就是 cntxt = null, 而uvm_root::get().get_full_name()为空字符串。其他情况都是以uvm_test_top为开头设置scope。
总结如下:test中set, driver中get, 如果socpe match,则可以get到set的资源。| code | scope |match | |:--|:--|--| | uvm_config_db#(int):: set(this,"env.agt.drv","val",10) | "uvm_test_top.env.agt.drv" | | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(this,"","val",value) |"uvm_test_top.env.agt.drv"| YES | | uvm_config_db#(int):: set(this,"env.agt*","val",10) | "uvm_test_top.env.agt*" | | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(null,"uvm_test_top.env.agt.drv_error_spell","val",value) |"uvm_test_top. env.agt.drv_error_spell"| YES | |uvm_config_db#(int):: set(null,"","val",10)| "" | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(null,"","val",value)|""| YES | |uvm_config_db#(int):: set(this,"env.agt","val",10)| "uvm_test_top.env.agt" | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(get_parent(),"","val",value)|"uvm_test_top.agt"| YES | |uvm_config_db#(int):: set(this,"env.agt.drv","val",10)| "uvm_test_top.env.agt.drv" | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(null,"","val",value)|""| NO | |uvm_config_db#(int):: set(this,"*drv","val",10)| "uvm_test_top.*drv" | uvm_config_db#(int):: get(null,get_full_name(),"val",value)|"uvm_test_top.env.agt.drv"| YES 由于第三个参数是string类型,书写错误时,编译不会报错,仿真如果不加上assert判断,也无法察觉错误,不利于debug。不过UVM中提供了check_config_usage print_config函数协助debug。
Verdi也提供了GUI界面,可以看到set get的具体内容,方便debug: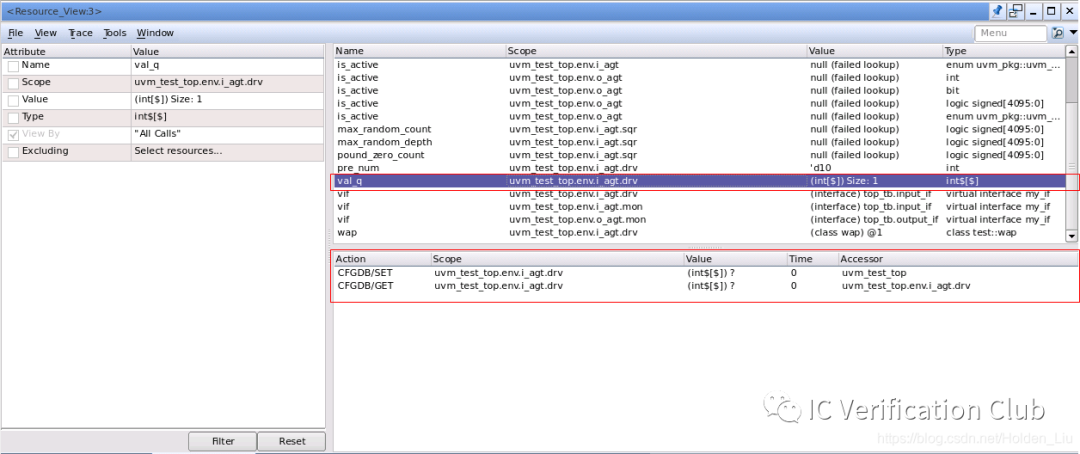
使用
uvm_config_db机制本质就是在一个地方创建资源,通过set以uvm_resource的形式存储到uvm_resource_pool上。然后在另一个地方,通过get获得之前创建的资源。
uvm_config_db机制还为资源加上了scope限制资源的访问,保证数据安全;precedence设置优先级;override资源重写;record记录资源访问历史用于debug等功能。
这里的资源可以是scalar objects class handles queues lists virtual interfaces 等。
队列,数组类型
对于队列,数组的传递,int val_q[$]直接通过uvm_config_db#(int) :: set(this, "env.i_agt.drv","val_q",val_q);的方式会编译报错,因为uvm_config_db#(type T=int)中type是int类型,而不是队列类型。需要typedef int t_q[$] ; 定义队列类型。 t_q val_q;uvm_config_db#(t_q) :: set(this, "env.i_agt.drv","val_q",val_q);
还有另一种方式,通过class封装队列(uvm已提供了uvm_queue#(type T)。这种方式的好处是,队列在一端改变,另一段也可以看到队列的修改,因为变量对资源的访问是通过句柄的形式,指向同一处资源。而直接传递队列,一端修改,另一端看不到,因为两端的队列是各自class scope中的两份不同的数据,只有再执行一次set get操作才会获得队列的新内容。
sequence中的资源访问
UVM中sequence不属uvm_component,存在固定的生命周期,对资源的访问,分为直接和间接两种类型。以reg_model为例,reg_model在env中create, sequence通过reg_model访问寄存器。
总结如下5种方式:
1.sequence没有出现在树形结构中,难以确定路径参数,可以通过set null, ""设定全局scope,这样sequence在哪里都可以访问资源。注意: sequence没有phase,get可以放在pre_body body pre_randomize pre_start中,只要在调用reg_model之前get被调用即可。
# env
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
m_regmodel = top_reg_model::create("m_regmodel");
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::set(null, "","reg_model",m_regmodel);
# seq
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::get(null, "","reg_model",m_regmodel);
// 为什么说 null, ""的组合是全局scope呢?
// TODO
1.sequence的路径可以通过get_full_name()获得。
# env
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
m_regmodel = top_reg_model::create("m_regmodel");
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::set(this, " agt.sqr.* ","reg_model",m_regmodel);
# seq
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::get(null, get_full_name(),"reg_model",m_regmodel);
1.sequence虽然不在树形结构上,但是其内部成员变量m_sequencer在树形结构上,可以通过m_sequencer间接访问资源。
# env
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
m_regmodel = top_reg_model::create("m_regmodel");
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::set(this, " agt.sqr","reg_model",m_regmodel);
# seq
top_reg_model m_regmodel;
uvm_config_db #(top_reg_model)::get(m_sequencer, "","reg_model",m_regmodel);
1.直接通过p_sequener访问资源。sequencer中get获得资源,sequence中调用p_sequencer.m_regmodel访问资源。2.直接赋值,在test中例化sequence时,seq.m_regmodel = m_regmodel。也可以封装到sequence中的function。
#seq
virtual function set_regmodel(top_reg_model m_regmodel);
this.m_regmodel = m_regmodel;
endfunction
当然也可以封装到test中的function:
#test
virtual function set_regmodel(sequence_baes seq);
seq.m_regmodel = m_regmodel;
endfunction
上述方法,本质都是一样的,将m_model句柄指向在env中创建的top_reg_model实例。
自定义资源池
我们也可以模仿uvm_event_pool uvm_resource_pool的方式,自定义一个资源池。
不使用uvm_config_db,自定义一个interface pool,示例如下(UVM实战 /ch10/section10.6/10.6.2):
# interface_pool
class if_object extends uvm_object;
`uvm_object_utils(if_object)
function new(string name = "if_object");
super.new(name);
endfunction
static if_object me;
static function if_object get();
if(me == null) begin
me = new("me");
end
return me;
endfunction
virtual my_if input_vif0;
virtual my_if output_vif0;
virtual my_if input_vif1;
virtual my_if output_vif1;
endclass
# top_tb.sv
module top_tb;
......
my_if input_if0(clk, rst_n);
my_if input_if1(clk, rst_n);
my_if output_if0(clk, rst_n);
my_if output_if1(clk, rst_n);
......
initial begin
if_object if_obj;
if_obj = if_object::get();
if_obj.input_vif0 = input_if0;
if_obj.input_vif1 = input_if1;
if_obj.output_vif0 = output_if0;
if_obj.output_vif1 = output_if1;
end
endmodule
# base_test.sv
class base_test extends uvm_test;
my_env env0;
my_env env1;
my_vsqr v_sqr;
function new(string name = "base_test", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(base_test)
endclass
......
function void base_test::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
if_object if_obj;
if_obj = if_object::get();
v_sqr.p_sqr0 = env0.i_agt.sqr;
v_sqr.p_sqr1 = env1.i_agt.sqr;
env0.i_agt.drv.vif = if_obj.input_vif0;
env0.i_agt.mon.vif = if_obj.input_vif0;
env0.o_agt.mon.vif = if_obj.output_vif0;
env1.i_agt.drv.vif = if_obj.input_vif1;
env1.i_agt.mon.vif = if_obj.input_vif1;
env1.o_agt.mon.vif = if_obj.output_vif1;
endfunction
平台中所有使用uvm_config_db的地方都可以通过这种方式替代,当然并不建议这样使用,uvm_config_db提供了更丰富的功能。这种方式的一个优点是编写错误可以在编译阶段发现,而uvm_config_db中字符串错误不容易发现。
wait_modified
uvm_config_db不仅可以共享资源,也可以像uvm_event那样,用于事件的同步,可以通过wait_modified实现。
drv0_seq在get之前,case0_vseq中必须先set,否则wait_modified会一直阻塞。因为wait_modified中调用@waiter.trigger,trigger是event类型;在set的最后,->w.trigger会触发该event。平台中所有的等待事件都放在了 m_waiters[string]中,其中的索引sting对应get set函数中第三个参数field_name。
class drv0_seq extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
......
virtual task body();
bit send_en = 1;
fork
while(1) begin
uvm_config_db#(bit)::wait_modified(null, get_full_name(), "send_en");
void'(uvm_config_db#(bit)::get(null, get_full_name, "send_en", send_en));
`uvm_info("drv0_seq", $sformatf("send_en value modified, the new value is %0d", send_en), UVM_LOW)
end
join_none
repeat (10) begin
`uvm_do(m_trans)
end
endtask
endclass
class case0_vseq extends uvm_sequence;
......
virtual task body();
my_transaction tr;
drv0_seq seq0;
drv1_seq seq1;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
fork
`uvm_do_on(seq0, p_sequencer.p_sqr0);
`uvm_do_on(seq1, p_sequencer.p_sqr1);
begin
#10000;
uvm_config_db#(bit)::set(uvm_root::get(), "uvm_test_top.v_sqr.*", "send_en", 0);
#10000;
uvm_config_db#(bit)::set(uvm_root::get(), "uvm_test_top.v_sqr.*", "send_en", 1);
end
join
#100;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
class m_uvm_waiter;
string inst_name;
string field_name;
event trigger;
function new (string inst_name, string field_name);
this.inst_name = inst_name;
this.field_name = field_name;
endfunction
endclass
class uvm_config_db#(type T=int) extends uvm_resource_db#(T);
......
// Internal waiter list for wait_modified
static local uvm_queue#(m_uvm_waiter) m_waiters[string];
......
static task wait_modified(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name,
string field_name);
process p = process::self();
string rstate = p.get_randstate();
m_uvm_waiter waiter;
if(cntxt == null)
cntxt = uvm_root::get();
if(cntxt != uvm_root::get()) begin
if(inst_name != "")
inst_name = {cntxt.get_full_name(),".",inst_name};
else
inst_name = cntxt.get_full_name();
end
waiter = new(inst_name, field_name);
if(!m_waiters.exists(field_name))
m_waiters[field_name] = new;
m_waiters[field_name].push_back(waiter);
p.set_randstate(rstate);
// wait on the waiter to trigger
@waiter.trigger;
// Remove the waiter from the waiter list
for(int i=0; iw.trigger;
end
end
......
endfunction
UVM_REGEX_NO_DPI
大量 ”滥用“ uvm_config_db配置访问资源,会降低仿真速度。 db:set/get()会自动扩展正则匹配,uvm_re_match()调用DPI的方式,增加仿真内核切换时间,每一次get()需要遍历set()的所有资源。而且不是简单的线性降低仿真速度。可以优化原有代码,减少set/get调用;使用UVM_REGEX_NO_DPI禁用正则匹配,仅仅使用* ? +这种简单的通配符。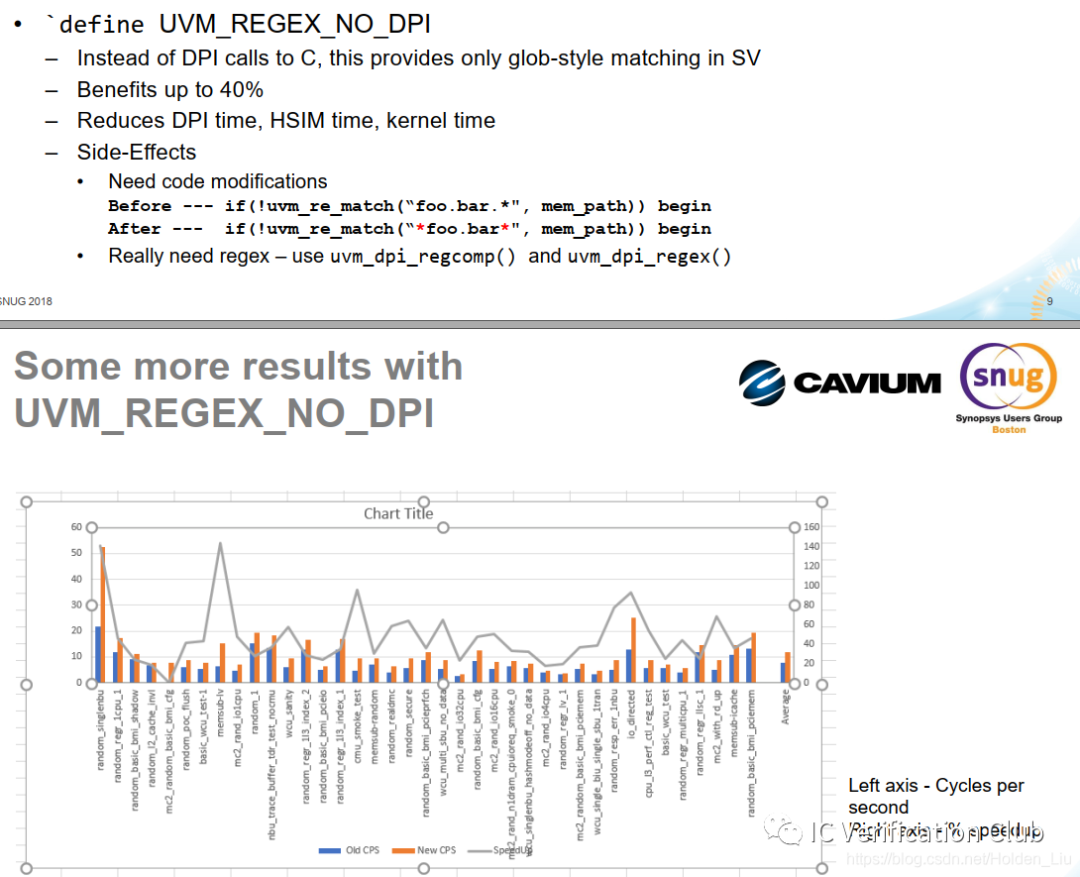
如果在SoC级别的平台,发现build_phase占用太多时间,可以参考SNUG 2018 Auditing the UVM Resource Database[4]进行优化,对源码进行相应修改,更好的Auditing平台的资源配置。
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !
